+31 (0)43 30 88 400 | office@comex.eu
Security and compliance in the financial sector
Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA).
As of January 2023, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) provides a new framework for the financial sector. This European regulation focuses on improving IT risk management, with the aim of increasing the resilience of financial organizations to cyber threats. The initiative is a response to the growing gap between increasing digital threats and the current level of operational resilience within the industry.
Who does DORA apply to?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) applies to a wide range of financial institutions within the European Union. These include banks, insurers, investment firms, payment institutions and pension funds. In addition, the regulations apply to IT service providers that provide critical services to these institutions, such as cloud providers and data center providers.
DORA aims to make not only financial organizations themselves, but also their entire chain of service providers more resilient to digital threats. This means that both large financial institutions and smaller players in the sector must meet stringent digital resilience and risk management requirements.


The 5 pillars of DORA
DORA is designed to strengthen the digital resilience of financial organizations and ensure that they are more resilient to IT incidents and cyber threats. The regulations are built around five core pillars:
- ICT risk management: Organizations should implement a solid framework to identify, manage and minimize digital risks.
- Incident reporting: Mandatory reporting of IT incidents to regulators to promote faster action and transparency.
- Testing digital resilience: Establish testing programs and conduct regular tests to identify and address vulnerabilities in systems.
- Third-party monitoring: Stricter monitoring of IT service providers, such as cloud providers, to reduce risks in the chain.
- Information sharing: sharing knowledge and threat information between organizations to increase joint resilience. This does need to take into account the potential sensitive nature of shared information.
The practical impact of DORA on organizations
DORA brings concrete changes to how financial institutions manage their digital infrastructure. The regulations require an in-depth review of IT systems and processes, with a focus on ensuring continuity and minimizing risk. In practical terms, this means that organizations must overhaul their entire IT landscape to comply with the requirements.
An important aspect of DORA is mandatory digital resilience testing. This means regularly exposing systems to
It is also necessary to make stricter agreements with IT service providers, such as cloud providers and data center providers. This means not only adjusting contracts, but also establishing clear procedures for oversight and monitoring. Organizations need to be sure that third-party providers meet the same high standards as themselves.
How data storage plays a crucial role at DORA
DORA places high demands on the data storage infrastructure of financial institutions. It is not just about keeping data safe, but also about ensuring flexibility, performance, compliance and security. These are some key areas:
Scalability: Storage solutions must be able to grow seamlessly with increasing data volumes, both on-premise and in cloud environments, without compromising on security.
Performance: DORA emphasizes the importance of short recovery times (RTO) and minimum data loss periods (RPO). Backups and recovery operations must be fast and reliable to ensure business continuity. Recovery should be a matter of hours, not days or even weeks.
Compliance: Storage solutions should support frameworks that allow organizations to demonstrate DORA compliance and testing requirements. Open systems often offer more flexibility and transparency.
Security: Security beyond software measures. In addition to
DORA requires not only a robust storage strategy, but also an approach that prepares the organization for rapid adaptation and compliance in an increasingly complex digital environment.
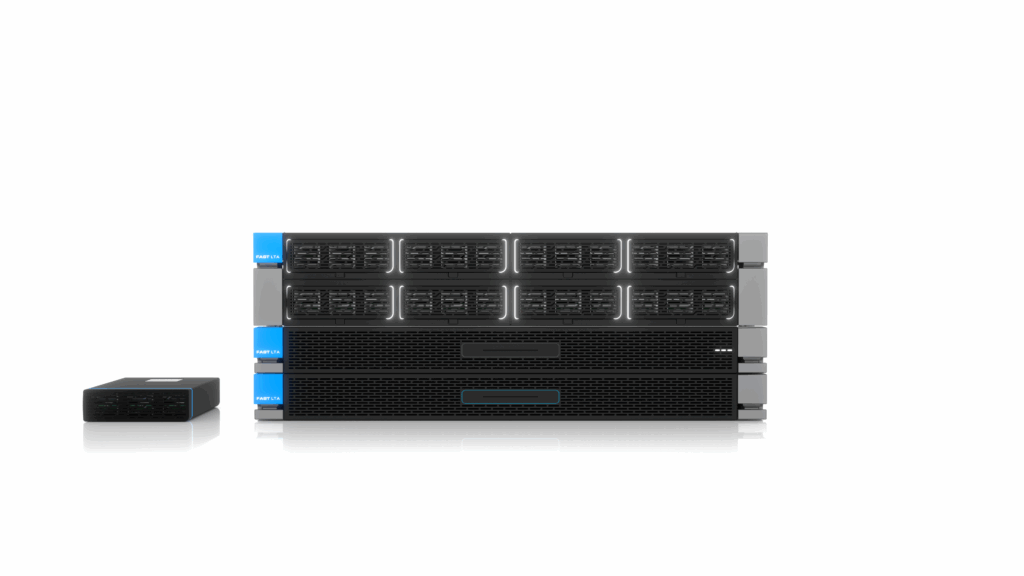
Storage that promotes DORA compliance
Ransomware proof backup and fast recovery
Secure your data against any threat
Protect your organization from data loss, ransomware and disruptions.
Thanks to our systems, you always have access to your data, even in case of emergencies.
Physical air gap as the most reliable layer of Immutability.
Long-term, compliant archiving
Comply with laws and regulations without compromise.
Certified hardware WORM storage for guaranteed immutability and Zero Loss.
Specially designed for sectors with critical infrastructures.